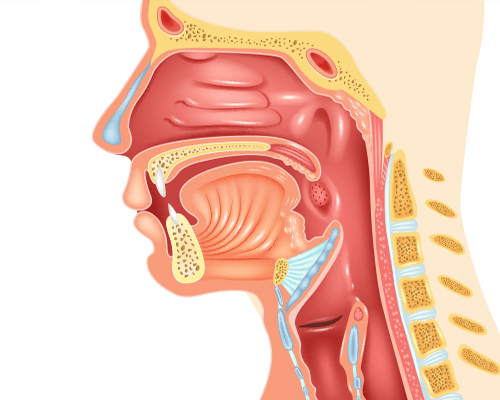
Head and neck cancer is a complex disease that requires a comprehensive diagnostic evaluation and sophisticated treatment. Cancers of the head and neck include those of the oral cavity, larynx (voice box), pharynx, salivary glands and nasal cavities. To help you make informed decisions about the journey ahead, it's important to educate yourself on the various types of head and neck cancer, including their symptoms, potential side effects and available treatments.
An increasing number of younger patients in their 40s and 50s are being diagnosed with the disease, largely because of a rise in human papillomavirus (HPV)-linked cancers. Still, more patients overall are surviving head and neck cancer, thanks in part to public health awareness efforts about tobacco uses the single largest risk factor for the diseases and advances in treatment options.
Head and neck cancer originates in the tissues and organs of the head and neck area. Most head and neck cancers begin in the squamous cells that line the mouth, nose and throat. These types of cancer are generally referred to as squamous cell carcinomas and may include cancer that develops in the larynx, throat, lips, mouth, nose or salivary glands.
The most common symptoms of head and neck cancer are swelling and a sore that doesn't heal. Other symptoms of head and neck cancer include voice changes or hoarseness, a neck mass, a sore throat that doesn't respond to an antibiotic, coughing up blood, trouble swallowing or breathing, a red or white patch in the mouth, frequent nose bleeds or unusual discharge, ear pain or trouble hearing, headaches and frequent coughing.
The five main types of head and neck cancer are classified according to the part of the body in which they develop: